About Uttar Pradesh
An Overview of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (UP), situated in the northern part of India, stands as the most populous state in the country.
Covering an area of approximately 243,286 square kilometers, UP is bounded by the states of Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh to the north, Haryana and Delhi to the west, Madhya Pradesh to the south, and Bihar to the east. This geographical positioning makes it a significant hub for trade and commerce in northern India.
Historically, Uttar Pradesh has been a crucible of Indian civilization, playing a pivotal role in shaping the country’s cultural and spiritual landscape. It is home to some of the most important religious sites, including Varanasi, one of the oldest inhabited cities in the world, and Ayodhya, believed to be the birthplace of Lord Rama. These cities attract millions of pilgrims and tourists alike, reinforcing UP's significance as a spiritual epicenter in India.
Politically, Uttar Pradesh also holds considerable influence; it has a substantial representation in the Indian Parliament and has been instrumental in the country’s political evolution. The state's complex socio-political dynamics stem from its diverse population, comprising various ethnic groups, languages, and religions, which contribute to its vibrant social fabric.
In addition to its historical and political importance, Uttar Pradesh offers a plethora of geographical diversity, ranging from the fertile plains of the Ganges to the rugged terrains of the Vindhya ranges. The state is also known for its agricultural outputs, being a major contributor to India's food production. This multifaceted identity of Uttar Pradesh makes it not only a significant region in India but also a fascinating area for exploration and discovery.
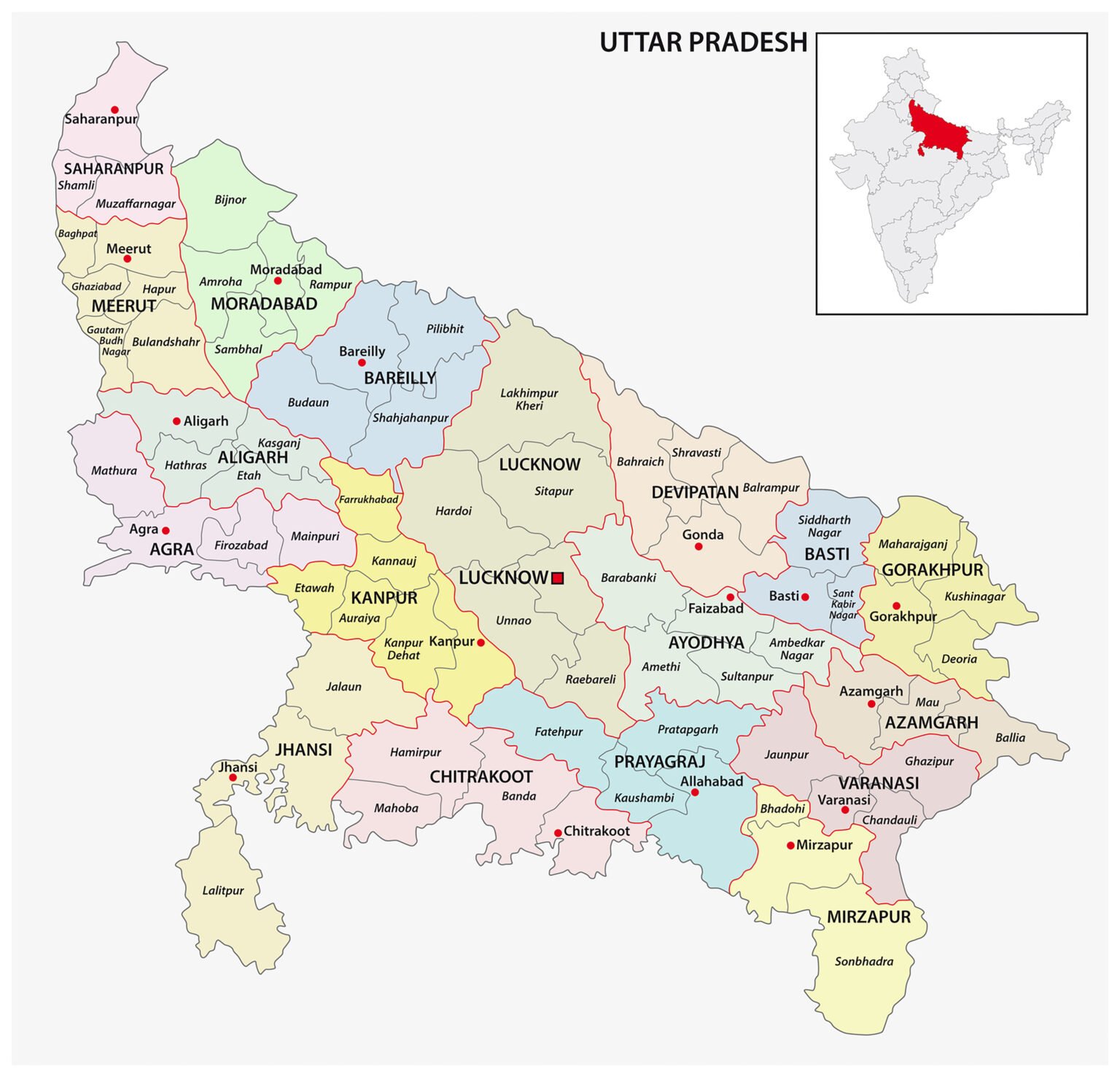
Map of Uttar Pradesh
A Brief History of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh, situated in North India, possesses a rich history. Historically known as the region of 'Aryavarta', it served as the cradle of numerous ancient civilizations and cultures. The recorded history of Uttar Pradesh can be traced to the Vedic period, wherein the area’s significance is noted in various Hindu scriptures. It was during the time of the Maurya Empire (322-185 BCE), with the reign of Emperor Ashoka, that Uttar Pradesh became a notable center for political and cultural advancements.
The illustrious Gupta Empire (circa 320-550 CE) marked another significant chapter in the region's history. It is often referred to as the Golden Age of India due to remarkable achievements in art, literature, and science. This period witnessed the flourishing of cities like Varanasi and Mathura, which stood as prominent cultural hubs. The region continued to evolve throughout the centuries, with various dynasties such as the Harsha, Pratihara, and later, the emergence of Rajput rulers, contributing to its rich mosaic of cultural heritage.
Transitioning into the Mughal era (16th-17th centuries), Uttar Pradesh became pivotal in the establishment of one of India's most influential empires. Cities like Agra and Fatehpur Sikri emerged as centers of power, where architectural marvels like the Taj Mahal were conceived. The Mughal period was characterized by an amalgamation of cultures, which left an indelible mark on the region’s identity.
In the 19th century, during the British colonial period, Uttar Pradesh underwent significant socio-political changes. The Revolt of 1857, which is often regarded as the first war of independence, was predominantly centered in this region, symbolizing the growing discontent against British rule. The formulation of Uttar Pradesh as a distinct state from the United Provinces occurred post-independence in 1950, marking a crucial milestone in shaping its political identity within India.
Geographical Features and Climate
Uttar Pradesh, a sprawling state in northern India, presents a remarkable geographical diversity characterized by its vast plains, navigable rivers, and notable landmarks. Encompassing an area of approximately 243,286 square kilometers, the state's landscape predominantly comprises the fertile Gangetic plains, a crucial agricultural zone underpinned by the consistent alluvial deposits from the Ganges River and its tributaries. Significant rivers such as the Yamuna, Ghaghara, and Gomti not only enhance the hydrological profile of the region but also support irrigation, thus bolstering the agricultural productivity that Uttar Pradesh is renowned for.
Additionally, the state's geographical makeup includes notable features like the Bundelkhand plateau, which is marked by its rugged topography and an arid climate that contrasts starkly with the lush, humid environment of the Gangetic plains. Prominent geographical landmarks such as the Vindhya Range and the Himalayan foothills in the north also contribute to its diverse landscape, each playing a vital role in the local ecosystem and influencing human settlement patterns.
Uttar Pradesh experiences a varied climate, ranging from a humid subtropical climate in the southern regions to a semi-arid climate in the western parts. Seasonal variations significantly impact agricultural practices, with the monsoon season bringing relief to farmers engaged in kharif crops, while rabi crops flourish during the cooler winter months. This climatic diversity also affects the lifestyle of residents, shaping cultural practices and festivals within the state. Moreover, the climate presents both challenges and opportunities for tourism, with seasonal variations offering a rich tapestry of experiences for visitors, from the vibrant festivities during winter to serene river experiences in the summer. Each season showcases a different facet of Uttar Pradesh, drawing both domestic and international tourists, and enhancing the state's vibrant culture and economy.
Demographics of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh, the most populous state in India, presents a complex demographic landscape that plays a key role in understanding its cultural and social dynamics. As of the latest census, the state's population is approximately 200 million, accounting for about 16% of India's total population. This figure positions Uttar Pradesh as one of the most significant contributors to the country's demographic profile.
The state's population is marked by considerable diversity, encompassing a variety of ethnic groups and communities. The majority are Indo-Aryan speakers, with the predominant ethnic groups including the Awadhi, Bhojpuri, and Braj communities. In addition to these dominant groups, Uttar Pradesh also hosts a range of tribal populations and underrepresented communities that contribute to the state's rich cultural tapestry.
Language usage further exemplifies this diversity. Hindi is the official language and is predominantly spoken, but several regional dialects, such as Urdu, Bhojpuri, and Braj, are also widely used across different parts of the state. This linguistic variety not only reflects the multicultural essence of Uttar Pradesh but also influences local governance, education, and media. Moreover, the state's religious landscape is equally multifaceted, with a majority of Hindus, alongside significant populations of Muslims, Sikhs, and Jains, among other religions. This pluralism creates a dynamic social environment that impacts the state's policies and community interactions.
The demographic factors of Uttar Pradesh are crucial in shaping its socio-economic policies. Understanding the population density in urban versus rural areas leads to informed decisions on resource allocation, infrastructure development, and social programs. As such, the diverse demographics of Uttar Pradesh highlight the importance of inclusive governance and policy-making to address the needs of its varied communities effectively.
Economic Overview of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh, one of India's largest states by population, boasts a diverse economic landscape that encompasses agriculture, industry, and services. The state plays a significant role in the agricultural sector, contributing to nearly one-fifth of India's total agricultural output. Key crops include sugarcane, wheat, rice, and pulses, positioning Uttar Pradesh as a leading producer of both food grains and cash crops. This agricultural strength forms the backbone of rural income and employment.
Industrial activity in Uttar Pradesh has also gained momentum, driven by the government's initiatives to boost investment and create a conducive environment for businesses. The state is home to several industrial hubs, including Noida and Greater Noida, which are known for their information technology and manufacturing sectors. Additionally, sectors such as textiles, electronics, and food processing are witnessing significant growth. The emergence of special economic zones and industrial parks further supports the industrial ecosystem in Uttar Pradesh.
The services sector in Uttar Pradesh is rapidly evolving, contributing to the state's GDP and employment. Key areas under this sector include hospitality, retail, banking, and telecommunications. The increasing urbanization and rising disposable incomes have fueled the demand for various services, promoting investment in infrastructure and service delivery. Moreover, Uttar Pradesh is witnessing a burgeoning startup ecosystem, with numerous enterprises and entrepreneurs emerging in recent years.
Despite its economic potential, Uttar Pradesh faces several challenges, including infrastructural deficits, unemployment in rural areas, and socio-economic disparities. The government has undertaken various initiatives to address these issues, such as enhancing connectivity, promoting skill development programs, and implementing policies to attract foreign direct investment. These efforts aim to foster sustainable economic growth and uplift the living standards of the population, establishing Uttar Pradesh as a significant player in India's broader economic landscape.
Cultural Heritage and Festivals
Uttar Pradesh, often hailed as the cultural heartland of India, boasts a rich tapestry of traditions that reflect a multitude of influences spanning centuries. The state is home to a vibrant artistic legacy, evidenced through various forms of art, music, and dance that have evolved over generations. Renowned for its classical dance forms such as Kathak, which flourished under the Mughal patronage, Uttar Pradesh provides an incredible window into the intricate dance movements and narratives that highlight the themes of divine love and human emotion.
Moreover, the region is celebrated for its traditional crafts, from intricate pottery and textiles to exquisite jewelry. The art of crafting beautiful Banarasi sarees is particularly famous, showcasing the skill and creativity of local artisans. Each piece not only represents high craftsmanship but also carries the historical and cultural significance of Uttar Pradesh’s rich heritage.
The architectural legacy of Uttar Pradesh is equally notable, with the presence of majestic historical monuments such as the Taj Mahal, Fatehpur Sikri, and the historic city of Varanasi. These structures epitomize the synthesis of various architectural styles, serving as a testament to the rich cultural amalgamation that has occurred over the years.
Furthermore, festivals in Uttar Pradesh are a vibrant spectacle that encapsulates the spirit of community and tradition. Major celebrations such as Diwali, Eid, Holi, and Dussehra see active participation from people of all backgrounds, reinforcing social bonds and fostering an inclusive environment. These festivals not only celebrate cultural diversity but also bring attention to the region's religious significance, promoting mutual respect among various ethnic groups.
Overall, the cultural heritage and festivals of Uttar Pradesh are not merely occasions of celebration but a profound expression of the state’s identity, intricately woven into the everyday lives of its inhabitants. This enduring legacy offers a glimpse into the harmonious coexistence of various traditions, arts, and communal ties that define this fascinating region.
Educational Institutions and Development
Uttar Pradesh (UP), as the most populous state in India, boasts a diverse educational infrastructure designed to cater to a wide range of academic pursuits. The state is home to several prominent universities, including Banaras Hindu University and Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia Avadh University, which offer undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral programs across various disciplines. Additionally, the presence of specialized institutions such as the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur underscores UP’s commitment to engineering and technology education. These universities not only contribute significantly to the higher education landscape but also have a profound influence on the socio-economic fabric of the region.
While higher education is notable, Uttar Pradesh also places emphasis on vocational training to enhance employability among its youth. Institutions like the Uttar Pradesh Technical University have introduced various skill development programs aimed at bridging the gap between education and employment. The government has launched several initiatives and policies to promote skill training, thereby enabling students to gain practical experience and relevant qualifications for the job market.
As for literacy rates, Uttar Pradesh has made notable strides in recent years. The state's literacy rate has gradually increased, now standing at around 67%, reflecting significant improvement in educational outreach and awareness. However, challenges such as regional disparities and access to quality education continue to persist, impacting the overall educational development of the state. Various reforms have been implemented to address these challenges, with initiatives aimed at reducing dropout rates, particularly among marginalized communities.
